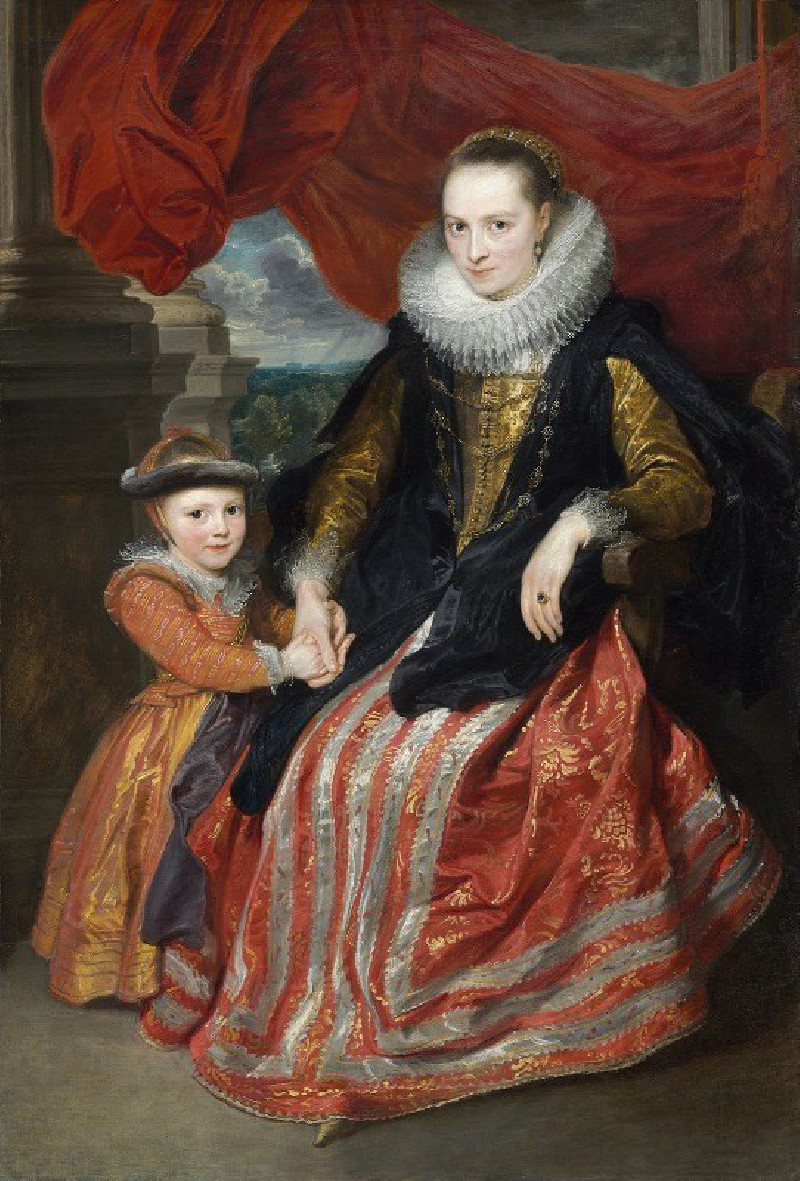
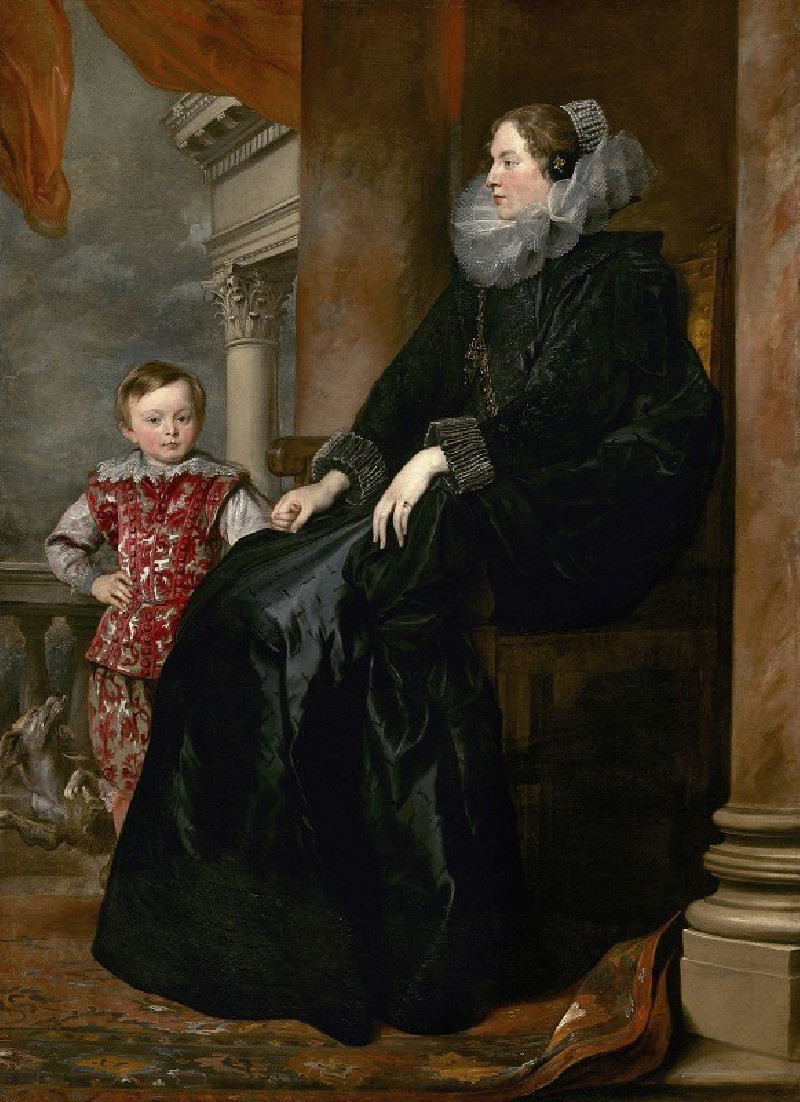
Susanna Fourment and Her Daughter (1621)
Technique: Giclée quality print
Recommended by our customers
More about this artwork
On our website, we are proud to showcase a masterpiece of portraiture from the Baroque era, "Susanna Fourment and Her Daughter" (1621) by the esteemed Flemish artist Anthony van Dyck. This captivating painting is a stunning example of Van Dyck's skill in capturing the grace and sophistication of his subjects, alongside his meticulous attention to detail and rich color palette.The painting presents Susanna Fourment, a member of a prominent Antwerp family, sitting regally beside her young daughter. The poised and elegant Susanna, draped in a luxurious black gown with intricate golden embroidery, exudes a serene confidence. Her attire includes a strikingly wide lace collar that frames her face, complementing her calm, composed expression.Beside her, her daughter, clad in a vibrant red and gold dress, holds her mother's hand, looking up with a gentle childlike curiosity. The contrast between Susanna's mature poise and her daughter's youthful innocence enhances the emotional depth of the painting.In the background, a rich red curtain and a glimpse of a tranquil landscape through a stone archway add layers of texture and color, setting a grand, yet intimate atmosphere.Through "Susanna Fourment and Her Daughter," Anthony van Dyck not only immortalizes the bond between mother and child but also crafts a vivid portrayal of wealth and fashion in 17th-century Antwerp. This painting is a testament to the artist's ability to weave personal character and broader cultural elegance into a single, harmonious composition.
Delivery
Returns
Sir Anthony van Dyck (1599 – 1641) was a Flemish Baroque artist who became the leading court painter in England after success in the Spanish Netherlands and Italy.
The seventh child of Frans van Dyck, a wealthy Antwerp silk merchant, Anthony painted from an early age. He was successful as an independent painter in his late teens, and became a master in the Antwerp guild in 1618. By this time he was working in the studio of the leading northern painter of the day, Peter Paul Rubens, who became a major influence on his work.