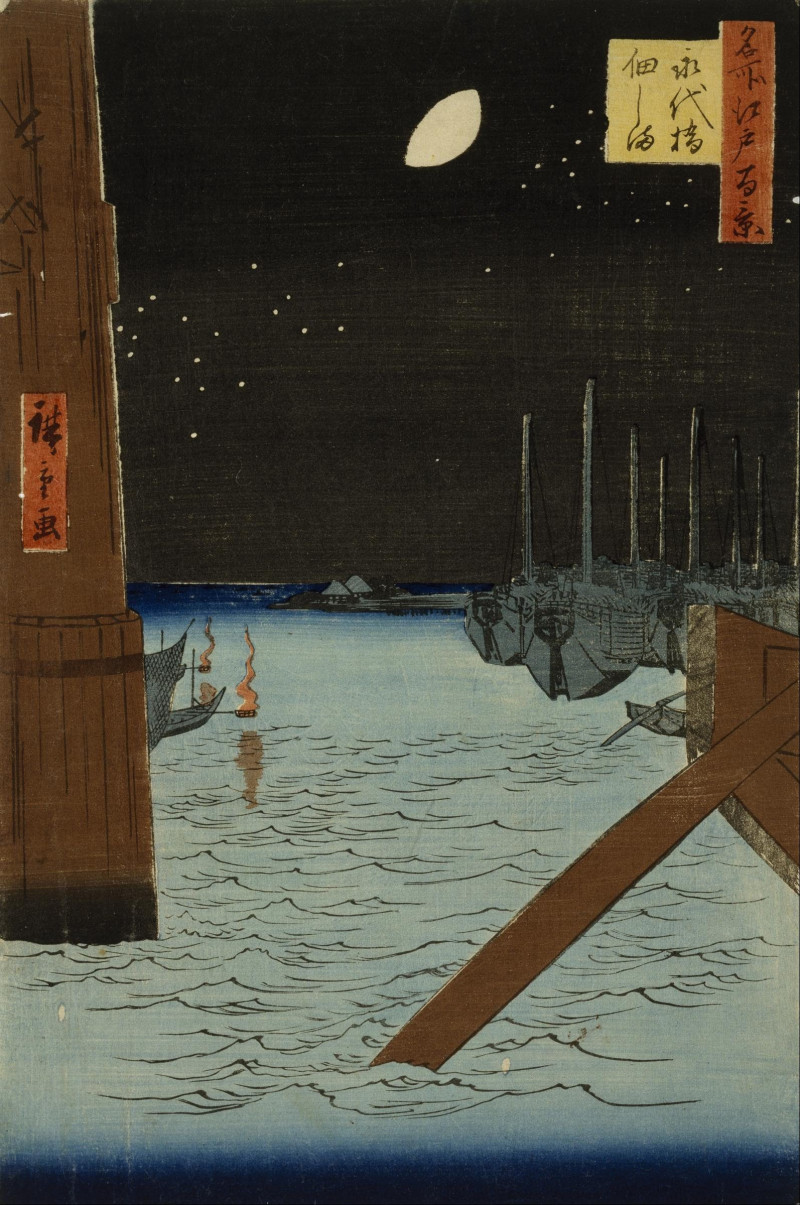
Downpour At Ohashi Bridge, Atake
More about this artwork
Delivery
Returns
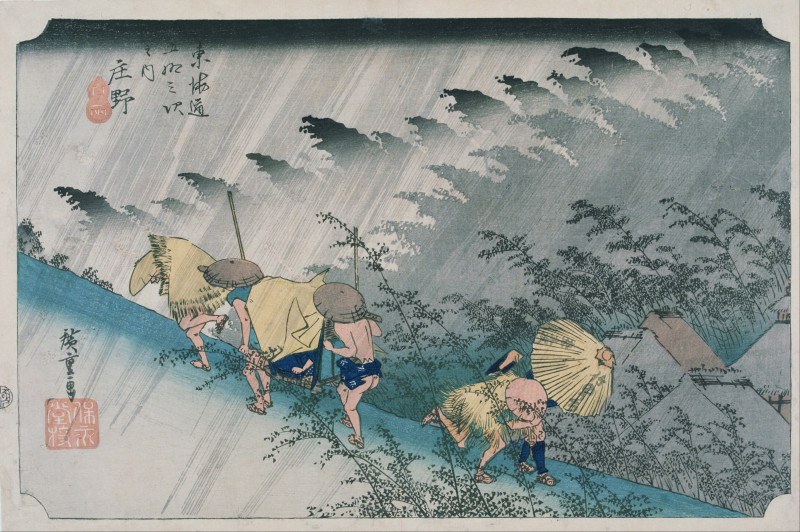
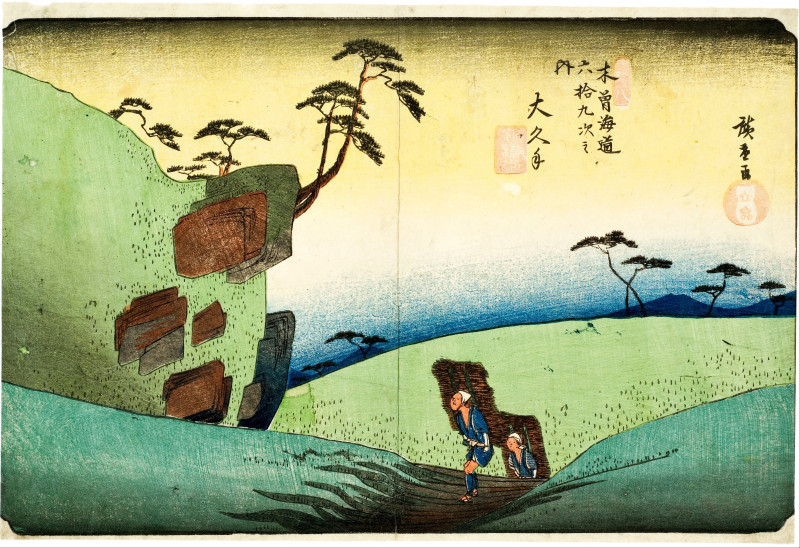
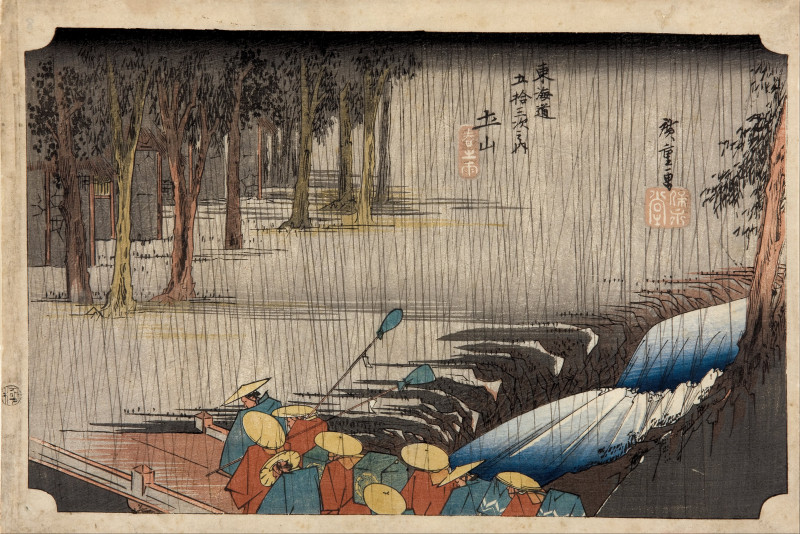
Utagawa Hiroshige (/ˌhɪəroʊˈʃiːɡeɪ/, also US: /ˌhɪərəˈ-/; Japanese: 歌川 広重 [ɯtaɡaɰa çiɾoɕiɡe]), born Andō Hiroshige (安藤 広重; 1797 – 12 October 1858), was a Japanese ukiyo-e artist, considered the last great master of that tradition.
Hiroshige is best known for his horizontal-format landscape series The Fifty-three Stations of the Tōkaidō and for his vertical-format landscape series One Hundred Famous Views of Edo. The subjects of his work were atypical of the ukiyo-e genre, whose typical focus was on beautiful women, popular actors, and other scenes of the urban pleasure districts of Japan's Edo period (1603–1868). The popular series Thirty-six Views of Mount Fuji by Hokusai was a strong influence on Hiroshige's choice of subject, though Hiroshige's approach was more poetic and ambient than Hokusai's bolder, more formal prints. Subtle use of color was essential in Hiroshige's prints, often printed with multiple impressions in the same area and with extensive use of bokashi (color gradation), both of which were rather labor-intensive techniques.
For scholars and collectors, Hiroshige's death marked the beginning of a rapid decline in the ukiyo-e genre, especially in the face of the westernization that followed the Meiji Restoration of 1868. Hiroshige's work came to have a marked influence on Western painting towards the close of the 19th century as a part of the trend in Japonism. Western artists, such as Manet and Monet, collected and closely studied Hiroshige's compositions. Vincent van Gogh even went so far as to paint copies of two of Hiroshige's prints from One Hundred Famous Views of Edo.